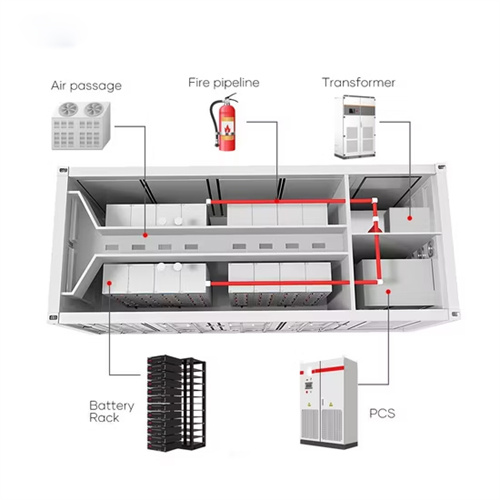
Principle of energy storage liquid constant temperature system

Introduction to thermal energy storage systems
Thermal energy storage (TES) systems can store heat or cold to be used later, at different conditions such as temperature, place, or power. TES systems are divided in three

Advances in battery thermal management: Current landscape and
Energy storage systems: Conduction through aluminum cooling plates in direct contact with a cold plate cooled by liquid coolant. Maximum temperature (2nd method) ∼39 °C

6.1: Freezing of Food
• The temperature of the freezing medium (ambient temperature) and storage remains constant (i.e., a steady-state situation). Step 1 Identify the type of heat processes and

Thermal Energy Storage
A characteristic of thermal energy storage systems is that they are diversified with respect to temperature, power level, and heat transfer fluids, and that each application is

12.2 First law of Thermodynamics: Thermal Energy and Work
where P is the pressure of a gas, V is the volume it occupies, N is the number of particles (atoms or molecules) in the gas, and T is its absolute temperature.The constant k is called the

Advances in thermal energy storage: Fundamentals and
Even though each thermal energy source has its specific context, TES is a critical function that enables energy conservation across all main thermal energy sources [5]

Review on Sensible Heat Storage System Principle, Performance and
The second disadvantages associated with the sensible heat storage system are that cannot store or deliver at constant temperature. Principle of sensible storage. In sensible

7.6: Conservation of Energy
The law of conservation of energy states that the total energy is constant in any process. but it is not possible to convert all the energy of a system to work. The efficiency (E_{ff}) of a machine or human is defined to be (E_{ff} =

Chapter 1: Thermodynamics for Thermal Energy Storage
Thermal energy storage processes often involve changes in temperature, volume and/or pressure. The relationship between these properties is therefore important for

Energy storage systems: a review
TES systems are divided into two categories: low temperature energy storage (LTES) system and high temperature energy storage (HTES) system, based on the operating

9.5: Conservation of Energy, the Work-Energy Principle, and the
Conservation of Energy, the Work-Energy Principle, and the Mechanical Energy Balance — These notes describe (1) how the Work-Energy Principle is developed from the Conservation

Analysis and Comparison of different types of Thermal Energy Storage
energy consumption can be reduced, more efficient systems can be facilitated and are cost effective. The share of renewable energy can be increased by the way of such thermal energy

Thermal Energy Storage
2.1 Physical Principles. Thermal energy supplied by solar thermal processes can be in principle stored directly as thermal energy and as chemical energy (Steinmann, 2020)

Comprehensive evaluation of a novel liquid carbon dioxide energy
A series of energy storage technologies such as compressed air energy storage (CAES) [6], pumped hydro energy storage [7] and thermal storage [8] have received

4.5: The first law of thermodynamics for closed systems
Internal Energy; Characteristic: Both heat and work are energy transfer mechanisms. They are not properties of a system. Internal energy is a property of a system. Interaction with the system: Both heat and work must cross the

Energy storage systems
During the phase transition, the storage material can absorb or release large amounts of energy at almost constant temperature. The storage capacity can be significantly increased by taking

Solid–Liquid Phase Equilibrium: Alkane Systems for Low-Temperature
The phase equilibrium studies for low-temperature energy storage applications in our group started with the work developed for the di-n-alkyl-adipates [].A new eutectic system

Thermal Energy Storage Systems
The operational principles of thermal energy storage systems are identical as other forms of energy storage methods, as mentioned earlier. A typical thermal energy storage

A technical feasibility study of a liquid carbon dioxide energy storage
Numerous innovative liquid CO 2 energy storage systems have also been proposed based on the a centrifugal pump, and a cold energy storage unit. The operational

Review and prospect of compressed air energy storage system
2.1 Fundamental principle. CAES is an energy storage technology based on gas turbine technology, which uses electricity to compress air and stores the high-pressure air

Thermodynamic Analysis of High‐Temperature Energy Storage Concepts
Among different technologies, pumped hydro energy storage systems represent the state of the art, with the largest installed capacity, but their potential is limited. 1 R&D projects on

Advanced Compressed Air Energy Storage Systems:
For example, liquid air energy storage (LAES) reduces the storage volume by a factor of 20 compared with compressed air storage (CAS). The working principle of

Introduction to Electrochemical Energy Storage | SpringerLink
1.2.1 Fossil Fuels. A fossil fuel is a fuel that contains energy stored during ancient photosynthesis. The fossil fuels are usually formed by natural processes, such as

Phase change material-based thermal energy storage
High-temperature thermal storage has been widely investigated in power plants for load shifting, in which thermal storage allows for operation at a constant power level even

Latent thermal energy storage technologies and applications: A
PCMs allow the storage of latent thermal energy during phase change at almost stable temperature. The article presents a classification of PCMs according to their chemical

Thermodynamic and economic analysis of a novel compressed air energy
The working principle of the CAES system is as follows: during charging, air at ambient temperature and pressure is compressed into high-pressure air by a compressor and stored in

(PDF) Latent Thermal Energy Storage Technologies and
The use of thermal energy storage (TES) in the energy system allows to conserving energy, increase the overall efficiency of the systems by eliminating differences

A perspective on high‐temperature heat storage using liquid
As an alternative solution, liquid metal-based heat storage systems are proposed. Liquid metal thermal energy storage systems are capable of storing heat with a

Thermal Storage: From Low-to-High-Temperature
Thermochemical heat storage is a technology under development with potentially high-energy densities. The binding energy of a working pair, for example, a hydrating salt and water, is used for thermal
Liquid–gas cryogenic energy storage units operating at constant temperature
A cryogenic Energy Storage Unit (ESU) is a closed system able to store thermal energy at low temperature without significant temperature drift [1] can be coupled to the cold

1 Basic thermodynamics of thermal energy storage
energy storage. 1.1.1 Sensible heat By far the most common way of thermal energy storage is as sensible heat. As fig.1.2 shows, heat transferred to the storage medium leads to a temperature

Review on operation control of cold thermal energy storage in
CTES technology generally refers to the storage of cold energy in a storage medium at a temperature below the nominal temperature of space or the operating

An overview of thermal energy storage systems | Request PDF
Latent heat thermal energy storage (LHTES) systems are a type of thermal energy storage technology that store and release energy through the phase transition of a

6 FAQs about [Principle of energy storage liquid constant temperature system]
What are the operational principles of thermal energy storage systems?
The operational principles of thermal energy storage systems are identical as other forms of energy storage methods, as mentioned earlier. A typical thermal energy storage system consists of three sequential processes: charging, storing, and discharging periods.
How is thermal energy stored?
Thermal energy can generally be stored in two ways: sensible heat storage and latent heat storage. It is also possible to store thermal energy in a combination of sensible and latent, which is called hybrid thermal energy storage. Figure 2.8 shows the branch of thermal energy storage methods.
What are the characteristics of thermal energy storage systems?
A characteristic of thermal energy storage systems is that they are diversified with respect to temperature, power level, and heat transfer fluids, and that each application is characterized by its specific operation parameters. This requires the understanding of a broad portfolio of storage designs, media, and methods.
How energy is stored in sensible thermal energy storage systems?
Energy is stored in sensible thermal energy storage systems by altering the temperature of a storage medium, such as water, air, oil, rock beds, bricks, concrete, sand, or soil. Storage media can be made of one or more materials. It depends on the final and initial temperature difference, mass and specific heat of the storage medium.
How is thermal energy storage performed based on heat changes?
As thermal energy storage is performed based on the heat changes in an energy storage medium, first, we need to define the branch of heat. There are two types of heat change in a material: sensible and latent heat. When energy is released from a material, the temperature of that material decreases.
What are the different types of thermal energy storage systems?
Thermal energy storage (TES) systems can store heat or cold to be used later, at different conditions such as temperature, place, or power. TES systems are divided in three types: sensible heat, latent heat, and sorption and chemical energy storage (also known as thermochemical).
Related Contents
- Energy storage tank liquid cooling
- Lithium battery energy storage principle diagram
- Schematic diagram of the switch principle of energy storage system
- Grid energy storage battery water cooling box principle
- Energy storage cabinet liquid cooling unit water pump pressure
- Detailed explanation of container liquid cooling energy storage system
- Principle of energy storage system power replenishment system
- Photovoltaic energy storage working principle diagram
- Installation of liquid cooling pipeline for energy storage battery cabinet
- How to install the liquid cooling energy storage module into the cabinet
- 210 degree liquid cooling energy storage cabinet quotation
- Principle of Microgrid Energy Storage System