The total energy storage E of the system is equal to

Handbook on Battery Energy Storage System
3.1ttery Energy Storage System Deployment across the Electrical Power System Ba 23 3.2requency Containment and Subsequent Restoration F 29 3.3uitability of Batteries for Short

Conservation of Energy
ΔE = K + U (The total energy is the sum of the kinetic and potential energies. From this, you can infer that for an isolated system, any change in kinetic energy will correspond in an equal but opposite change in

Total to Build the Largest Battery-based Energy Storage Project
Total launches a battery-based energy storage project in Mardyck, at the Flandres Center, in Dunkirk''s port district. With a storage capacity of 25 megawatt hours

7.6: Conservation of Energy
The law of conservation of energy states that the total energy is constant in any process. Energy may change in form or be transferred from one system to another, but the total remains the same. When all forms of energy are

What is a total energy?
The total energy of the system of a block and a spring is equal to the sum of the potential energy stored in the spring plus the kinetic energy of the block and is proportional to the square of the amplitude ETotal=(1/2)kA2.

15.3: Energy in Simple Harmonic Motion
The total energy of the system is constant. A closer look at the energy of the system shows that the kinetic energy oscillates like a sine-squared function, while the potential energy oscillates like a cosine-squared function. However, the

Energy Change Online Practice Flashcards
Which equation best expresses the total initial energy E of the system? and more. Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like When modeling a system in physics,

Energy in SHM | CIE A Level Physics Revision Notes
A simple harmonic system is therefore constantly converting between kinetic and potential energy When one increases, the other decreases and vice versa, therefore: The total energy of a simple harmonic system

8.4: Energy Stored in a Capacitor
In a cardiac emergency, a portable electronic device known as an automated external defibrillator (AED) can be a lifesaver. A defibrillator (Figure (PageIndex{2})) delivers a large charge in a

14.5 Mechanical Energy and Conservation of Mechanical Energy
The total change in the mechanical energy of the system is defined to be the sum of the changes of the kinetic and the potential energies, Δ E = Δ K + Δ U .

7.6: Conservation of Energy
Commonly encountered forms of energy include electric energy, chemical energy, radiant energy, nuclear energy, and thermal energy. Energy is often utilized to do work, but it is not possible to convert all the energy of a system to work.

VII. SOME BASICS OF THERMODYNAMICS A. Internal Energy U
In Thermodynamics, the total energy E of our system (as described by an empirical force field) is called internal energy U. U is a state function, which means, that the energy of a system

Energy Storage Calculator
The change in the total energy of a system during a process from states 1 to 2 can be expressed as [Delta E = E_2 - E_1 ={}_{1}Q_{2} - {}_{1}W_{2}] If the changes in the kinetic and potential energies of the system are negligible, i.e.,

Problem 7 Must the total energy of a syste [FREE SOLUTION]
The principle of conservation of energy is broader than just mechanical energy conservation; it encompasses all forms of energy within a closed system. This principle asserts that the total

What is total energy formula?
How do you calculate work and energy? The total energy of the system of a block and a spring is equal to the sum of the potential energy stored in the spring plus the kinetic energy of the block and is proportional to the

7.4: Work Done on a System By All the External Forces
Now consider the total system formed by A+B. Assuming it is a closed system, its total energy must be constant, and so any change in the total energy of B must be equal and opposite the

A Simple Note on the Total Mechanical Energy of the System
Observe that at all points A,B, and C, total mechanical energy is, E mechanical = mgh. Therefore, it is said that total mechanical energy is conserved. Conclusion. The total mechanical energy

Conservation of Energy | Edexcel GCSE Physics Revision
The total energy transferred in to a system must be equal to the total energy transferred out of the system. Therefore, energy is never ''lost'' but it can be transferred to the surroundings. Energy can be dissipated (spread out)

When Hamiltonian and the total energy are the same
Tour Start here for a quick overview of the site Help Center Detailed answers to any questions you might have Meta Discuss the workings and policies of this site

11.4
The most general way to compute the total energy stored in a system is to integrate the energy densities given by (3) and (5) over the volumes of the respective systems. If systems can be
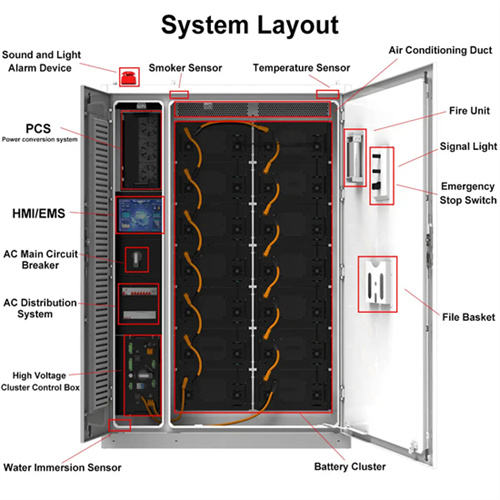
4.2: Internal energy in a system
[E=U+KE+PE] [e=u+ke+pe] where, and represent the total energy, internal energy, kinetic energy, and potential energy of a system, respectively;, and are their corresponding specific

Introduction to energy storage
The authors conclude that an optimal solution balancing curtailment and storage may result in storage requirements approximately equal to the daily average demand. (1),

MODULE-1 ELECTROCHEMISTRY AND ENERGY STORAGE SYSTEM
Free energy: It is the thermodynamic state, a part of a total energy of a system is converted into work and the rest is unavailable. Discover the world''s research 25+ million

Total Mechanical Energy: Definition & Formula
Now if a system is isolated, the total energy of the system remains constant because nonconservative forces are excluded and the net work done on the system is equal to zero.

14.5 Mechanical Energy and Conservation of Mechanical Energy
The total change in the mechanical energy of the system is defined to be the sum of the changes of the kinetic and the potential energies, ΔE = ΔK + ΔU . (14.4.17) sys For a closed system

The total energy of the system is:
The total energy of the system is:. Ans: Hint: The system''s total energy is the total kinetic and gravitational potential energy, and this whole energy is conserved in orbital motion. One

13.4: Gravitational Potential Energy and Total Energy
More generally, it is the speed at any position such that the total energy is zero. If the total energy is zero or greater, the object escapes. If the total energy is negative, the object cannot escape.

1st Law of Thermodynamics
The internal energy would also increase if work were done onto a system. Any work or heat that goes into or out of a system changes the internal energy. However, since

Conservation of Energy
This division of the universe into a system and its surroundings can also be applied to the total energy in the universe. In equation format: [math]displaystyle{ E_{total,
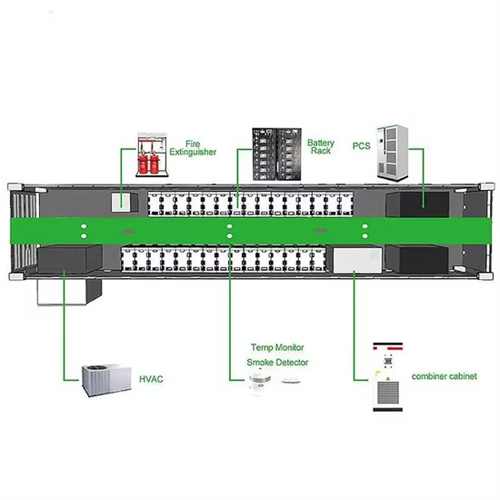
The value of long-duration energy storage under various grid
Long-duration energy storage (LDES) is a key resource in enabling zero-emissions electricity grids but its role within different types of grids is not well understood.

Energy storage and transmission expansion planning: substitutes
binary variable that is equal to 1 if energy storage unit s was built in a previous year and its investment return period is not completed, and 0 otherwise; binary variable that is
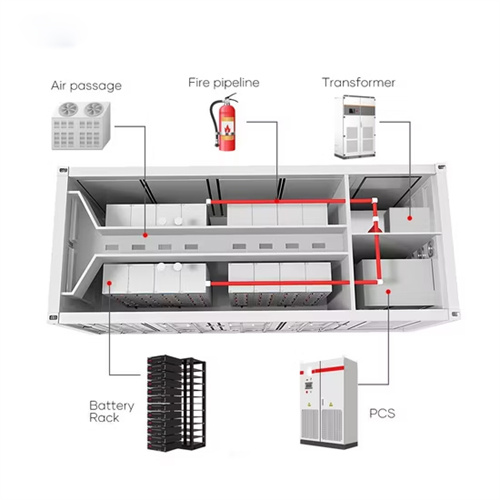
8.2: Internal Energy and First Law of Thermodynamics
That is, the total energy of a system plus its surroundings is constant, which must be true if energy is conserved. The state of a system is a complete description of a system at a given time,

Decarbonizing power systems: A critical review of the role of energy
For example, an analysis of the European power system shows that with levelized cost of storage (LCOS) — i.e. total lifetime cost of investment and operation of the

When is the first integral equal to the total energy of the system?
The difficulty here is apparently relating the intuitive definition of energy that we know from "everyday" Newtonian mechanics, to the first integral of the equations of motion.

11.4
11.4 Energy Storage. In the conservation theorem, (11.2.7), we have identified the terms E P/ t and H o M / t as the rate of energy supplied per unit volume to the polarization and

6 FAQs about [The total energy storage E of the system is equal to]
Is the total energy of a system constant?
The total energy of the system is constant. A closer look at the energy of the system shows that the kinetic energy oscillates like a sine-squared function, while the potential energy oscillates like a cosine-squared function. However, the total energy for the system is constant and is proportional to the amplitude squared.
How is energy stored in a system calculated?
This tutorial will explain these principles and their interconnectedness in more detail. The energy (E) stored in a system can be calculated from the potential difference (V) and the electrical charge (Q) with the following formula: E: This is the energy stored in the system, typically measured in joules (J).
What is energy storage?
Energy storage refers to the methods by which energy is stored for later use. The electrical charge is a fundamental property of matter that results in electromagnetic interactions. The potential difference, also known as voltage, is the work done per unit charge.
Does a system have a total energy and an internal energy?
A system possesses a total energy and an internal energy. Both heat and work are path functions; their magnitudes depend on the states and the specific process path. Internal energy is a state function; its magnitude depends on the state only.
What is energy stored per unit volume?
This function is the energy stored per unit volume, because the energy supplied per unit volume expressed by the integral is a function of the final value D of the displacement flux, and we assumed that the fields E and D were zero at t = -. Here, D represents the differential of D, usually denoted by dD.
What are the principles of energy storage?
The principles of energy storage, electrical charge, and potential difference are vital components in the field of electricity and magnetism, a subfield of physics. Energy storage refers to the methods by which energy is stored for later use. The electrical charge is a fundamental property of matter that results in electromagnetic interactions.
Related Contents
- Total energy storage formula for a thermodynamic system
- How to calculate the total power of the energy storage system
- What is the total assembly price of photovoltaic energy storage cabinets
- Domestic Photovoltaic Energy Storage Bidding Announcement
- What are the parameters related to energy storage system
- Customs classification of lithium battery energy storage cabinets
- Wind power off-grid energy storage system
- Aluminum Energy Storage Box Quote Inquiry
- 1500w home energy storage system power supply
- Diy photovoltaic energy storage battery
- Does the photovoltaic villa have energy storage
- How to install energy storage cabinet industrial air conditioner